As businesses scale across borders and adopt digital-first operating models, managing people has become more complex than ever. From traditional enterprises to software-driven firms and crypto-native organizations, HR Management now plays a strategic role in stability, compliance, and long-term growth. It is no longer limited to hiring and payroll; instead, it sits at the intersection of technology, regulation, and organizational culture.
This guide explains what HR management is, how it has evolved in modern organizations, and why it matters for small companies, large enterprises, and fast-growing digital businesses operating in a global environment.
Understanding HR Management in Simple Terms
HR Management refers to the structured approach organizations use to manage their workforce effectively. It covers the policies, systems, and practices involved in recruiting, developing, compensating, and retaining employees while ensuring legal and operational compliance.
At its core, HR management focuses on aligning people-related decisions with business objectives. This alignment becomes especially important as companies grow, operate remotely, or expand into new markets.
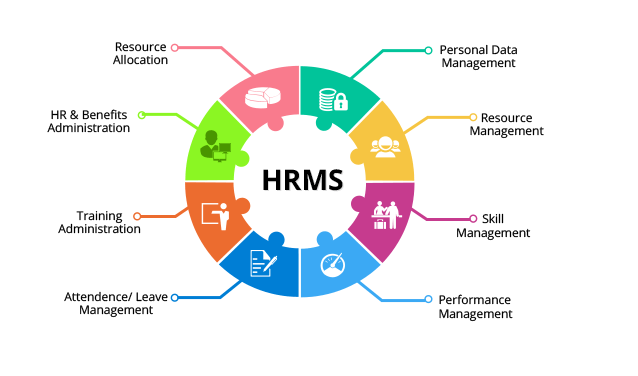
Core Functions of HR Management
Modern HR management extends far beyond administrative tasks. Its core functions typically include:
1. Recruitment and Talent Acquisition
Identifying, evaluating, and onboarding the right talent is foundational. In competitive markets, poor hiring decisions can slow execution and increase costs.
2. Employee Onboarding and Training
Structured onboarding ensures employees understand company processes, culture, and expectations from day one. Ongoing training supports skill development and adaptability.
3. Compensation and Benefits Administration
HR management oversees salary structures, incentives, benefits, and performance-linked rewards, ensuring fairness and consistency across roles and regions.
4. Performance Management
Clear goal-setting, evaluations, and feedback mechanisms help organizations track productivity and support employee growth.
5. Compliance and Risk Management
Employment laws vary by country and region. HR management ensures organizations comply with labor regulations, data protection standards, and workplace policies.
How HR Management Has Evolved
Historically, HR was viewed as a back-office function focused on record-keeping. Today, it has become a strategic discipline driven by technology and data.
Several trends have shaped this evolution:
- Digital transformation replacing manual processes with centralized systems
- Remote and hybrid work models becoming mainstream
- Global hiring increasing regulatory and operational complexity
- Data-driven decision-making influencing workforce planning
These shifts are particularly visible in technology-driven sectors, including software development and blockchain-based businesses, where teams are often distributed across multiple jurisdictions.
HR Management in a Global and Remote Work Era
Remote work is no longer an exception. Many organizations now operate with employees and contractors spread across different countries and time zones.
In this context, HR management supports:
- Standardized policies for global teams
- Clear documentation of roles and responsibilities
- Consistent onboarding regardless of location
- Visibility into workforce costs and headcount
For digital-first companies, especially those operating in fast-moving sectors like crypto and fintech, strong HR management reduces operational friction and supports scalability.
The Role of HR Management in Technology-Driven Organizations
Software companies, startups, and blockchain-related firms often grow rapidly. This growth can strain internal processes if HR management is not structured early.
In practice, organizations rely on formal HR Management frameworks such as those discussed in industry-focused analyses like HR Management to centralize workforce data, support compliance, and maintain operational clarity as teams expand.
This approach is increasingly viewed as essential rather than optional.
HR Management and Crypto Market Context
While HR management is not a crypto-specific concept, its importance has increased alongside the professionalization of the blockchain industry.
Recent market cycles have shown that:
- Rapid hiring during growth phases can expose structural weaknesses
- Market downturns require disciplined workforce planning
- Regulatory scrutiny demands accurate documentation and compliance
As crypto companies mature, many adopt traditional HR management practices to improve transparency and resilience, particularly when engaging with institutional partners or regulators.
Benefits of Strong HR Management
Well-implemented HR management offers several practical advantages:
- Operational efficiency: Reduced administrative overhead
- Regulatory compliance: Lower legal and financial risk
- Employee retention: Clear policies and growth paths
- Scalability: Easier expansion into new markets
- Data visibility: Better workforce planning and forecasting
For both small businesses and large enterprises, these benefits contribute to long-term stability.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, HR management is not without challenges.
Common Issues Include:
- Over-standardization that reduces flexibility
- Complexity when managing diverse employment models
- Upfront investment in systems and processes
- Resistance to formal structures in early-stage companies
Organizations must balance structure with adaptability, particularly in innovative or decentralized environments.
HR Management Tools and Systems
Most modern organizations rely on digital platforms to support HR management. These systems typically integrate:
- Employee records
- Payroll coordination
- Attendance and leave tracking
- Performance reviews
- Compliance reporting
While tools vary in sophistication, their purpose remains the same: creating a single source of truth for people-related operations.
HR Management for Small vs Large Organizations
Small Companies
- Focus on foundational policies and compliance
- Prioritize flexibility and cost efficiency
- Often combine HR roles with operations or finance
Large Enterprises
- Require formalized processes and reporting
- Manage complex hierarchies and global compliance
- Rely heavily on integrated HR systems
Regardless of size, the principles of HR management remain consistent, even as implementation differs.
Future Outlook: HR Management in a Digital Economy
Looking ahead, HR management is expected to become more data-driven and integrated with emerging technologies. Potential developments include:
- Greater automation of routine HR tasks
- Improved workforce analytics
- Integration with digital identity and compliance tools
- Increased focus on remote work governance
For organizations operating in fast-evolving industries, adapting HR management practices will be essential to remain competitive and compliant.
Conclusion
HR Management has evolved into a strategic function that supports organizational stability, scalability, and compliance in a global, digital economy. From small businesses to large enterprises and technology-driven firms, effective HR management helps align people, processes, and business goals.