United States In Situ Hybridization Market Size & Forecast 2026–2034
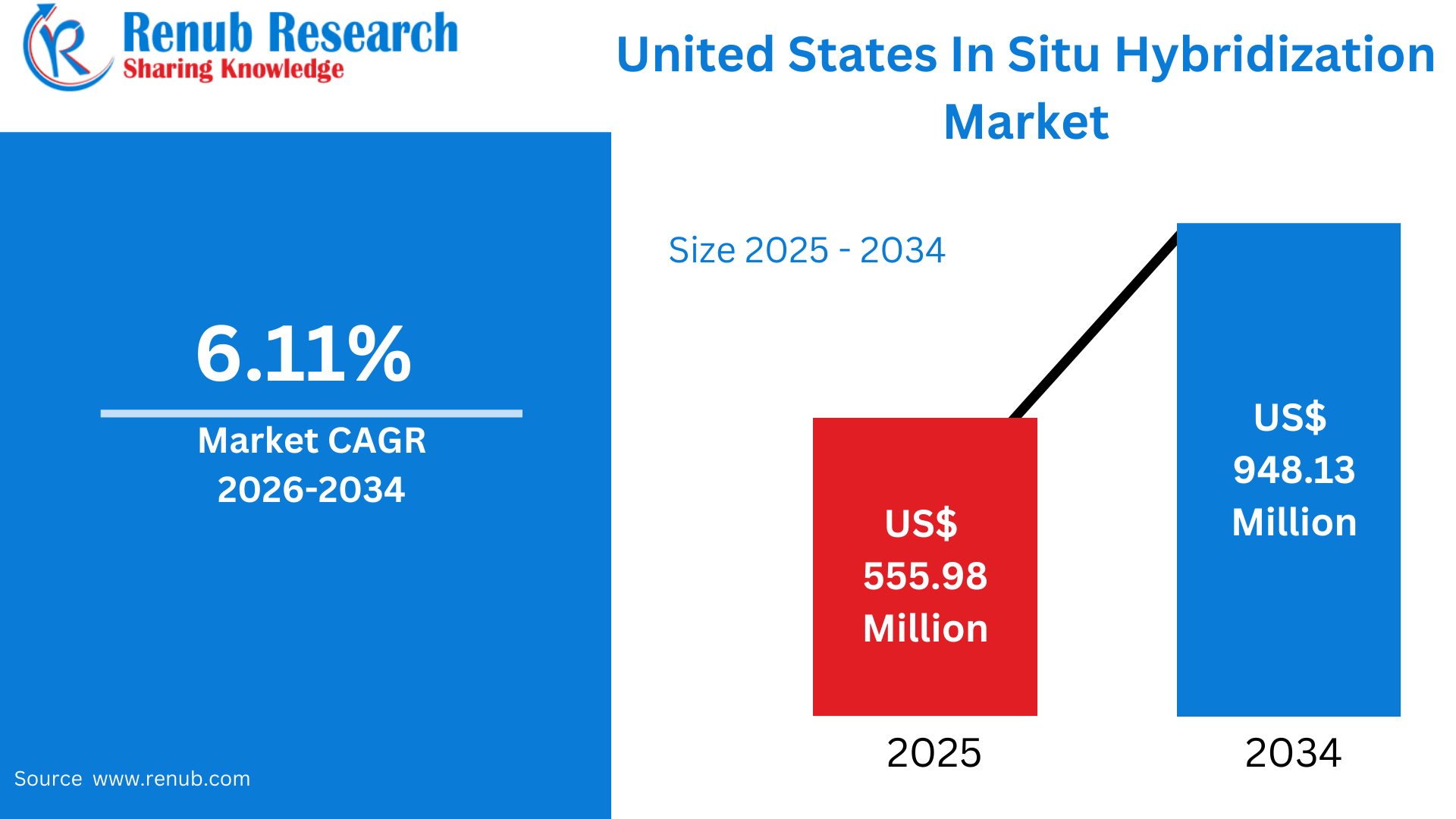
According to Renub Research United States In Situ Hybridization (ISH) market is anticipated to demonstrate strong and consistent growth over the forecast period, driven by the rapid adoption of advanced molecular diagnostic techniques across clinical and research settings. The market, valued at US$ 555.98 million in 2025, is projected to reach US$ 948.13 million by 2034, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.11% from 2026 to 2034. This growth is underpinned by expanding applications in oncology, genetic and rare disease diagnostics, infectious disease research, and the broader integration of precision medicine into U.S. healthcare systems.
In situ hybridization has evolved into a cornerstone technology for spatially resolved molecular analysis. Its ability to localize nucleic acid sequences directly within tissue architecture provides diagnostic and research insights that cannot be fully replicated by sequencing or PCR-based methods alone. As demand increases for tissue-level molecular context to support personalized treatment decisions, ISH is expected to remain a critical tool in the U.S. biomedical landscape.
Download Free Sample Report:https://www.renub.com/request-sample-page.php?gturl=united-states-in-situ-hybridization-market-p.php
United States In Situ Hybridization Market Outlook
In Situ Hybridization is a molecular technique used to detect and localize specific DNA or RNA sequences within intact cells, tissues, or chromosomes. The method relies on labeled nucleic acid probes that hybridize to complementary target sequences, enabling visualization of gene expression patterns, chromosomal abnormalities, and pathogen presence while preserving tissue morphology. Major variants include Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) and Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization (CISH), both of which offer high sensitivity and spatial resolution but differ in workflow, instrumentation, and interpretive approaches.
In the United States, ISH has gained significant traction due to the strong shift toward precision medicine, early disease detection, and biomarker-driven therapeutic strategies. Oncology remains the dominant application area, where ISH is routinely used to identify gene amplifications, translocations, and expression profiles that guide targeted therapies and immunotherapies. Beyond oncology, ISH is widely used in neuroscience, infectious disease pathology, developmental biology, and translational research. Continuous advancements in automation, probe design, multiplexing, and digital imaging have improved assay accuracy, reproducibility, and scalability, enabling broader adoption across both academic and diagnostic laboratories.
Growth Drivers in the United States In Situ Hybridization Market
Rising Adoption of Precision Oncology and Biomarker-Guided Therapies
The rapid expansion of precision oncology is one of the most influential drivers of ISH market growth in the United States. Modern cancer treatment increasingly depends on biomarker identification to determine patient eligibility for targeted therapies and companion diagnostics. ISH techniques, particularly FISH and CISH, are essential for detecting gene amplifications, chromosomal translocations, and copy-number variations that directly inform therapeutic decision-making.
Pathologists and oncologists rely on ISH to stratify patients, validate actionable mutations, and resolve ambiguous results from sequencing or immunohistochemistry. Multidisciplinary tumor boards place high value on the spatially resolved molecular data provided by ISH, which links genetic alterations to tumor morphology. The growing pipeline of targeted oncology drugs and immunotherapies that require molecular confirmation continues to propel clinical demand for robust tissue-based assays across U.S. cancer centers.
Advances in Automation, Imaging, and Probe Design
Technological innovation is significantly accelerating the adoption of ISH across U.S. laboratories. Automated staining platforms, standardized hybridization systems, and improved workflow integration have reduced hands-on time and inter-laboratory variability, making ISH more accessible to medium- and high-volume diagnostic centers. Advances in probe chemistry, including higher specificity, enhanced signal amplification, and multiplexing capabilities, have expanded the range of detectable targets, including low-abundance RNA transcripts.
Digital pathology and high-resolution imaging systems further enhance ISH workflows by enabling whole-slide scanning, quantitative analysis, and AI-assisted interpretation. These capabilities support remote consultation, centralized data management, and reproducible reporting, which are increasingly important in large healthcare networks and clinical trials. Improved fluorophores and imaging optics also allow complex multiplex FISH assays, increasing diagnostic depth while preserving tissue integrity.
Increasing Clinical and Research Investment in Molecular Pathology
Sustained investment in molecular pathology research and diagnostics is another major driver of ISH market growth. Federal funding, academic research grants, and private-sector investments in genomics, translational medicine, and companion diagnostic development continue to expand laboratory capacity across the United States. Clinical trials increasingly incorporate spatial molecular endpoints that rely on ISH to validate gene expression patterns, tumor heterogeneity, and microenvironment interactions.
At the clinical level, growing awareness among physicians of the diagnostic and prognostic value of tissue-based molecular assays is driving higher test-ordering volumes for oncology, infectious diseases, and genetic disorders. The expansion of centralized reference laboratories and pathology networks has further scaled ISH testing by offering specialized services to community hospitals and outpatient facilities. Education and training initiatives in molecular diagnostics continue to foster adoption among pathologists and laboratory professionals.
Challenges in the United States In Situ Hybridization Market
High Cost of Equipment, Reagents, and Skilled Labor
Despite its clinical utility, ISH adoption is constrained by high implementation and operational costs. Automated slide stainers, high-resolution fluorescence microscopes, whole-slide scanners, and advanced image analysis software require substantial capital investment. Consumables such as specialized probes, labeled nucleotides, amplification kits, and quality control materials can be costly on a per-test basis, particularly for multiplex assays.
ISH workflows also require highly trained histotechnologists and molecular pathologists for assay execution and result interpretation. Recruiting and retaining such skilled personnel adds to operational costs, making in-house ISH capabilities challenging for smaller hospitals and community laboratories. As a result, many institutions rely on centralized reference labs, which can increase turnaround times and logistical complexity. Variability in reimbursement for complex molecular tissue assays further complicates economic sustainability.
Technical Complexity, Standardization, and Interpretation Variability
ISH assays are technically demanding and sensitive to pre-analytical and analytical variables. Tissue fixation quality, embedding practices, and section thickness can significantly influence probe accessibility and signal quality. Differences in probe design, hybridization conditions, and amplification strategies may introduce variability across laboratories.
Interpretation of ISH results often requires expert judgment, particularly in borderline cases or heterogeneous tumors, leading to potential interobserver variability. Multiplex assays add complexity related to spectral separation and signal quantification. While efforts toward standardization and external quality assessment are ongoing, the absence of universally adopted protocols for all ISH applications remains a challenge for reproducibility and scalability.
United States In Situ Hybridization Market by Segment
Analytical Instruments Market
The U.S. ISH analytical instruments market includes automated slide stainers, fluorescence microscopes, hybridization ovens, whole-slide scanners, and image analysis software. Automation improves throughput and reproducibility, enabling laboratories to manage rising testing volumes driven by oncology diagnostics and clinical trials. Integrated systems that combine staining, imaging, and analysis streamline workflows, reduce turnaround time, and support regulatory compliance. Demand is growing for compact, user-friendly instruments that allow mid-sized laboratories to internalize ISH testing.
United States Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Market
FISH remains the most widely used ISH technique in the United States due to its high sensitivity and spatial resolution. It is a standard tool in oncology and genetic diagnostics for detecting chromosomal rearrangements, gene amplifications, and RNA targets. Clinical reliance on FISH for applications such as HER2 amplification testing, ALK and ROS1 rearrangements, and hematologic malignancies drives steady demand. Multiplex FISH and improved fluorophores continue to expand assay capabilities and throughput.
United States Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization Market
CISH combines nucleic acid detection with brightfield microscopy, allowing results to be interpreted using standard pathology equipment. The technique produces permanent, durable staining that integrates seamlessly with routine histology, making it particularly attractive for community hospitals and laboratories with limited fluorescence infrastructure. CISH remains widely used for HER2 testing and other applications where ease of interpretation and long-term archiving are priorities.
Infectious Diseases In Situ Hybridization Market
ISH plays a complementary role in infectious disease diagnostics by enabling direct visualization of pathogen nucleic acids within tissue context. This is particularly valuable for organisms that are difficult to culture or when PCR results require histologic correlation. ISH supports diagnosis in transplant pathology, neuropathology, and granulomatous disease and is widely used in research to study pathogen distribution and tissue reservoirs.
Genetic and Rare Disorders In Situ Hybridization Market
ISH is important in diagnosing genetic and rare disorders where spatial localization of gene expression or chromosomal abnormalities is critical. It is used in prenatal and neonatal pathology, mosaic conditions, and developmental anomalies. In rare disease research, ISH helps map aberrant expression patterns, supporting biomarker discovery and therapeutic development.
Diagnostic Laboratories Market
Diagnostic laboratories—including large reference labs, hospital-based pathology departments, and academic centers—form the backbone of the U.S. ISH service market. Centralized laboratories invest heavily in automation, validated panels, and quality systems to offer high-throughput testing. Hospital laboratories maintain in-house ISH capabilities for urgent oncology and surgical pathology cases, while partnerships with pharmaceutical companies support clinical trials and companion diagnostics.
State-Wise Market Outlook
California leads the U.S. ISH market due to its concentration of academic institutions, biotech companies, and major oncology centers. New York follows closely, driven by large medical centers, research hospitals, and reference laboratories. Washington benefits from a growing biotech sector and collaborative research environment, while Arizona shows steady growth supported by expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing access to molecular pathology services.
Market Segmentation
Product: Analytical Instruments, Probes, Kits & Reagents, Software & Services, Other Products
Technique: Fluorescence ISH (FISH), Chromogenic ISH (CISH), Amplified RNA-ISH, In-situ Sequencing
Application: Cancer Diagnostics & Research, Infectious Diseases, Genetic & Rare Disorders, Neurological & Developmental Biology, Others
End User: Diagnostic Laboratories, Academic & Research Institutes, Pharma-Biotech & CROs, Veterinary & Environmental Labs
Competitive Landscape and Company Analysis
The U.S. In Situ Hybridization market is competitive, with major players focusing on automation, probe innovation, multiplexing, and digital pathology integration. Key companies include PerkinElmer, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., BioView, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Merck KGaA, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Oxford Gene Technology IP Limited, Neogenomics Laboratories, Inc., and Advanced Cell Diagnostics, Inc..
Conclusion
The United States In Situ Hybridization market is positioned for strong growth through 2034, driven by precision oncology, expanding molecular pathology infrastructure, and continuous technological innovation. While high costs and technical complexity remain challenges, advancements in automation, imaging, and probe design continue to improve accessibility and clinical value. As tissue-based molecular insights become increasingly central to diagnostics and research, ISH will remain a vital technology shaping the future of precision medicine in the United States.